Benefits of Soil Health Testing
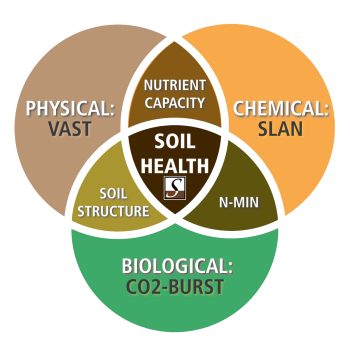
Traditional soil tests measure the physical and chemical properties of soil while soil health tests have a microbiological component for a more complete soil assessment.
By digging deeper into the physical, chemical and biological interactions we can make improved agronomic recommendations for higher yields and greater profit.

Establish a Baseline

Accurate Results
Improved recommendations
Soil Health Tests

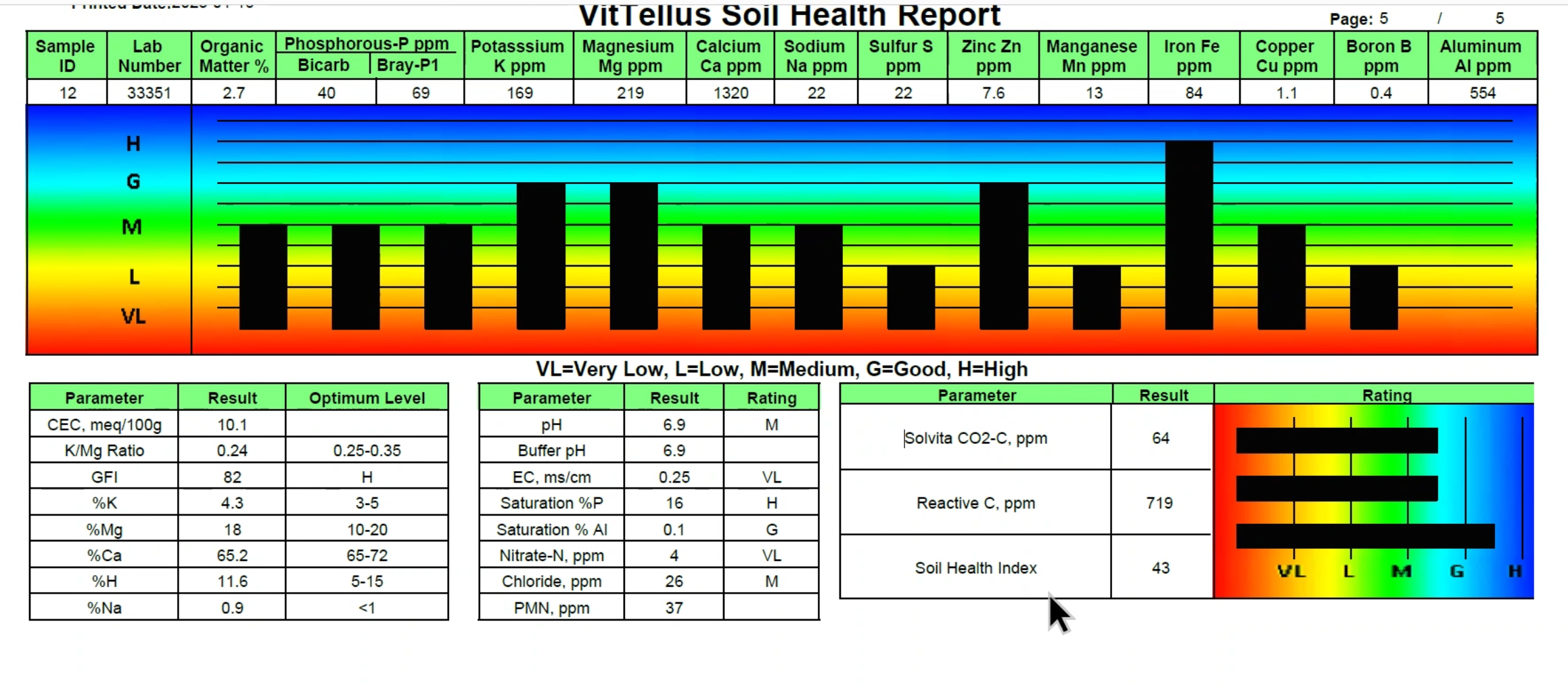
Vitellus® Soil Health Test
A&L Canada Laboratories supports farmers and crop consultants to improve soil health through research, information, soil management recommendations and education.
Traditional soil tests measure the physical and chemical properties of soil, and that is valuable, but soil is a living, dynamic and continually changing ecosystem and requires a more holistic approach with a microbiological component for a more complete soil assessment and allowing to make improved agronomic recommendations. The biological composition of the soil reflects the presence of disease suppressing and bio-stimulating microorganisms in the rhizosphere.
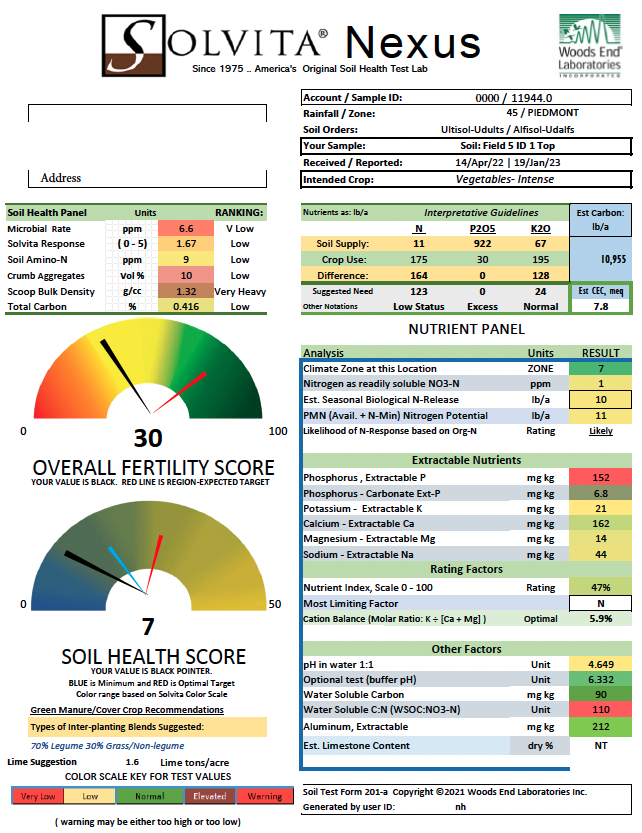
Solvita® Soil Health Test
Soil Health is an emerging concept of soil fertility which includes biological traits like microbial respiration in equal footing with nutrient chemistry.
Solvita® soil tests capture these key biological, chemical and physical traits indicating healthy functioning in a farm system.
Ways to Improve your Soil Health
Taken from post from Soil Optix (need to reword): https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7054522083321511936/
1. Soil Analysis
You can’t manage what you don’t measure! Soil analysis helps to set a baseline for parameters such as pH, nutrient levels, organic matter content, and so much more.
2. Nutrient Management Planning
NMP involves carefully monitoring and managing fertilizer use to minimize waste and maximize soil health. This practice can reduce the risk of nutrient leaching and runoff.
3. Precision Agriculture
Precision Agriculture uses advanced technology such as drones, sensors, and GPS to create detailed maps of crop health, moisture levels, and nutrient needs. This data can be used to make more informed decisions about crop management and soil health.
4. Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative agriculture builds soil health and resilience through practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and reduced tillage. This can help sequester carbon, reduce erosion, and improve soil fertility.
Treat your soil like royalty, and reap the rewards! Are you ready to have your soil bring home the gold?
Soil Health Videos
Soil Health FAQs
A: Soil health refers to the overall condition of the soil, including its physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is important because healthy soil supports plant growth, biodiversity, water retention, nutrient cycling, and carbon sequestration, contributing to sustainable agriculture and ecosystem resilience.
A: You can improve soil health by practicing soil conservation techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, reduced tillage, adding organic matter (compost, manure), managing soil pH, and using soil amendments based on soil test results.
A: Key factors include soil texture, structure, organic matter content, nutrient levels (NPK), pH balance, microbial activity, water infiltration, and soil biodiversity.
A: Yes, soil health testing can identify nutrient imbalances and soil health issues, allowing for more precise fertilizer applications and integrated pest management strategies, ultimately reducing input costs and environmental impacts.
A: Healthy soil supports vigorous root development, nutrient uptake, disease resistance, and water retention, leading to improved crop yield, quality, and resilience to environmental stresses.